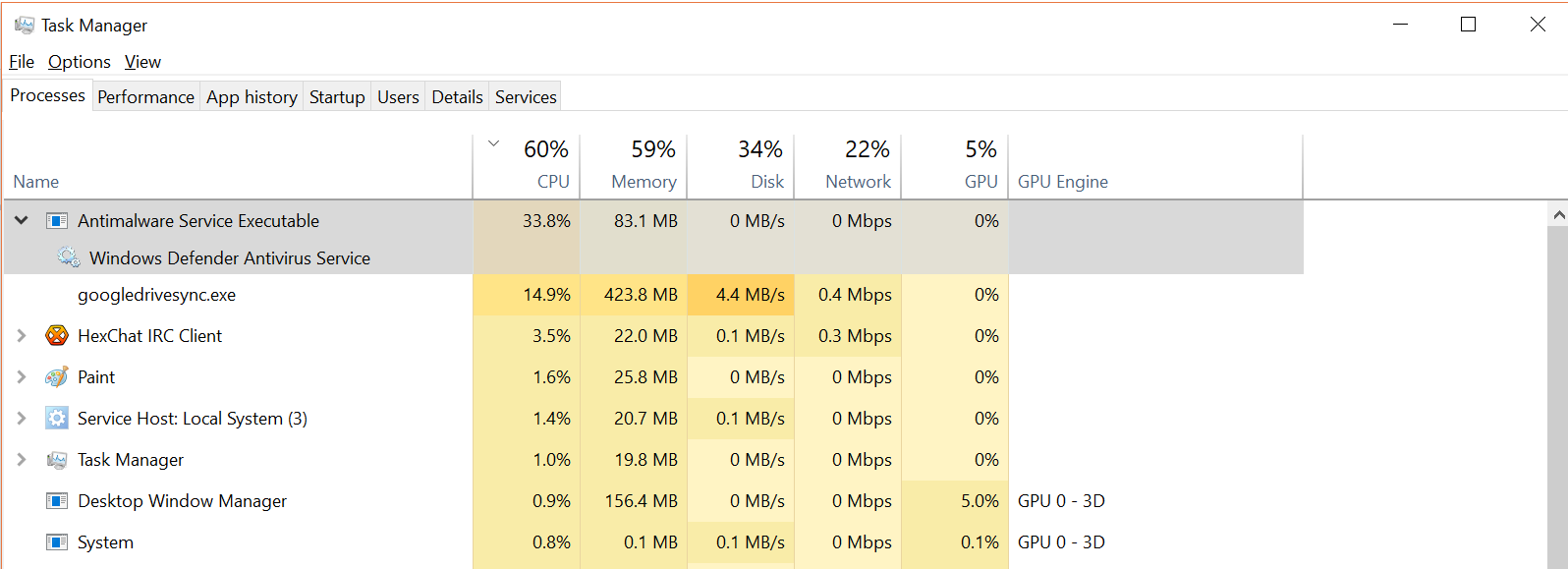
Antimalware Service Executable is a background process of Windows 10 built-in antivirus program, Windows Defender which is performing background scans to check for dangerous files and programs when you are trying to access different files. It is also known as MsMpEng.exe and it is a part of Windows OS, performing its duty in the background and making sure that you don’t open any malware file accidentally.
This background process uses computer resources such as disk, CPU, RAM, and even network bandwidth and sometimes it can take a huge amount of these resources and completely drain them, making your PC slow. This can happen anytime but mostly it happens when you get a Windows update. After that, this background process has high CPU/Disk usage that can be checked from the Task Manager.
If you happen to face this problem where the Antimalware Service Executable is using high CPU/Disk resources then worry not, it can be easily dealt with, and here are a few fixes to this problem.
Fix 1: Changing Windows Defender’s Schedule
Sometimes, this problem is caused by real-time protection of Windows Defender and it can be fixed by changing the Windows Defender’s scan schedule. Here is how you can change Windows’s Defender’s Scan Schedule and fix this problem:
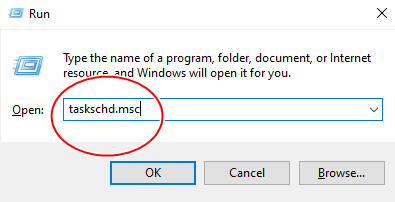
- Open the Run box by pressing Windows + R key at the same time.
- Type taskschd.msc and hit the Enter key.
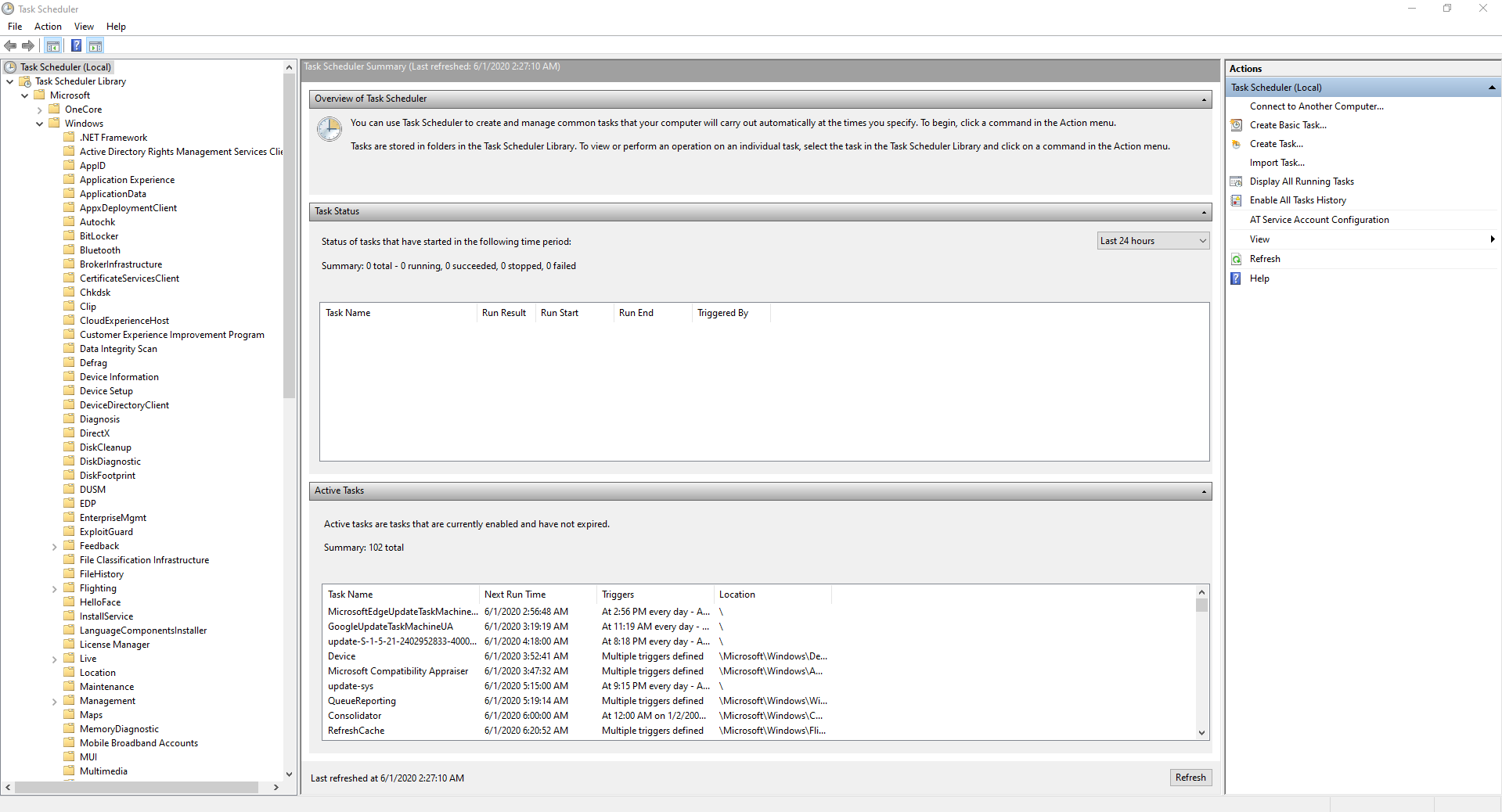
- Go to Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows.
- Scroll down and click on Windows Defender.
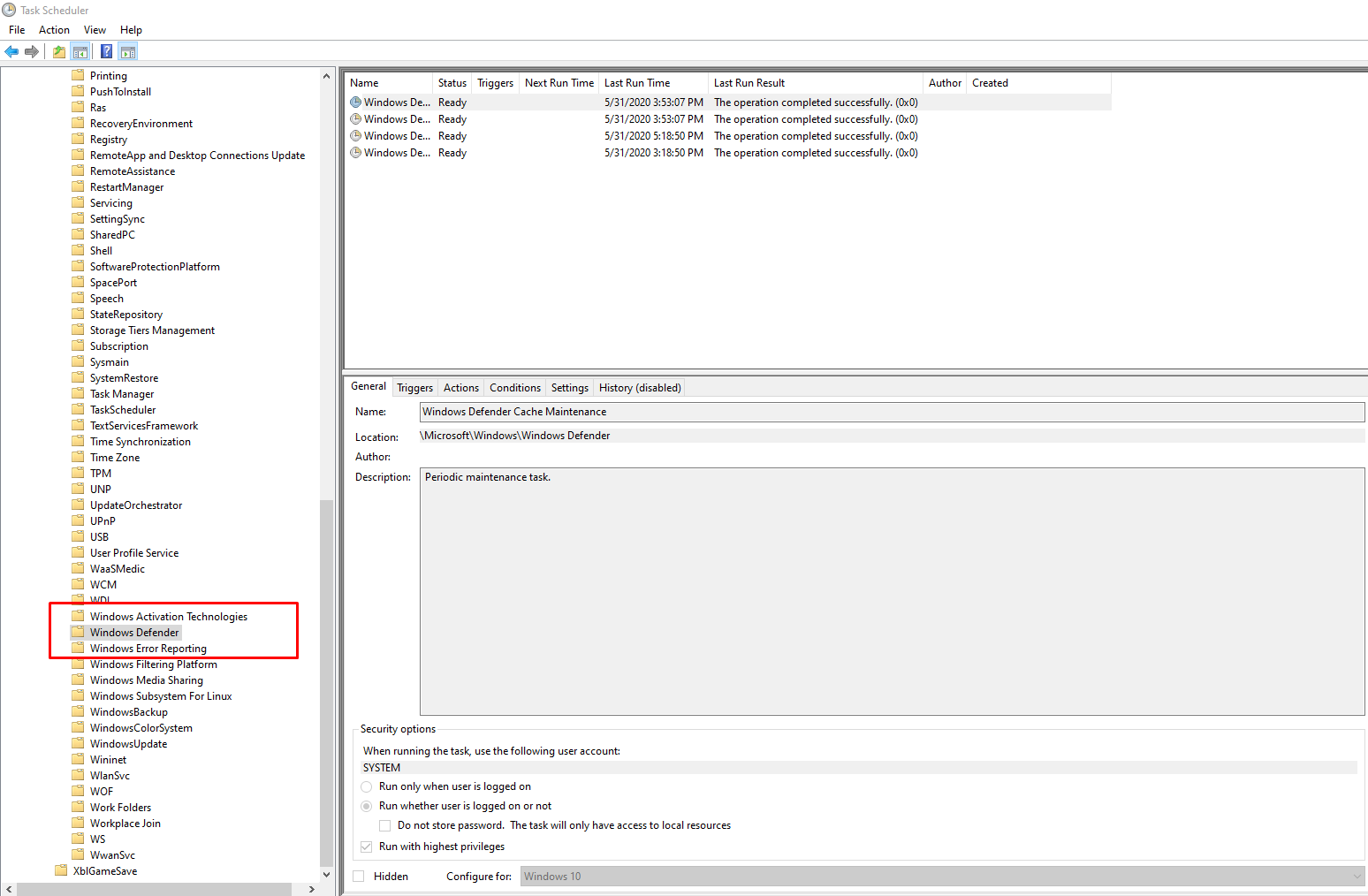
- Click on the Windows Defender Scheduled Scan option.
- Uncheck the Run with highest privileges checkbox.
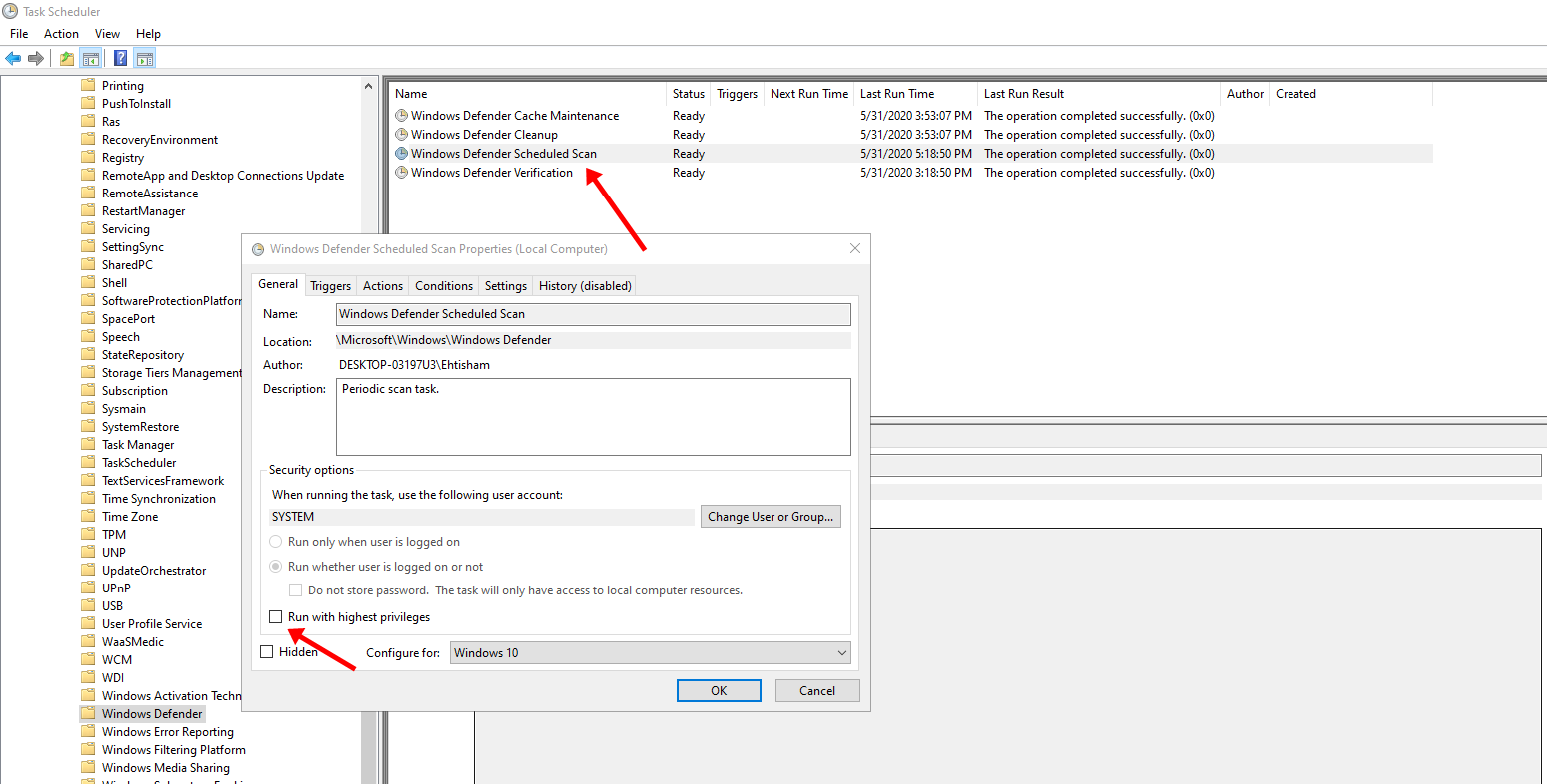
- Go to the Conditions tab and uncheck all the checkboxes.
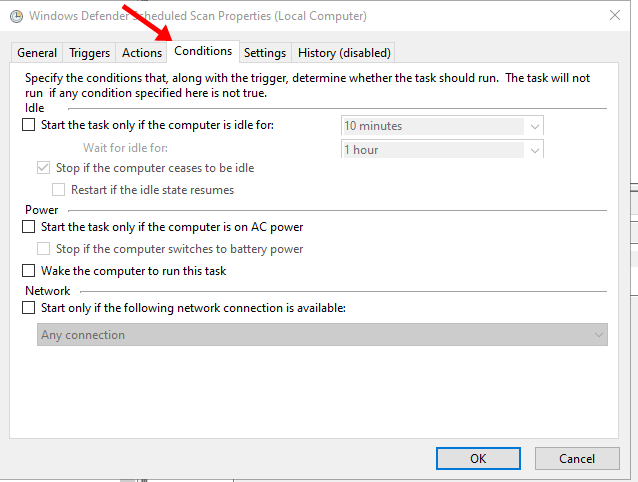
- Click OK.
Following the aforementioned should help you fix this problem but if this didn’t work and the problem still persists then move on to the second fix.
Fix 2: Adding Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender’s Exclusion List
Adding Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender’s Exclusion List can also help fix this problem. Here is how you can add Antimalware Service Executable to Windows Defender’s Exclusion List:
- Open the Windows Settings by pressing Windows + I key at the same time.
- Click on the Update and security option.
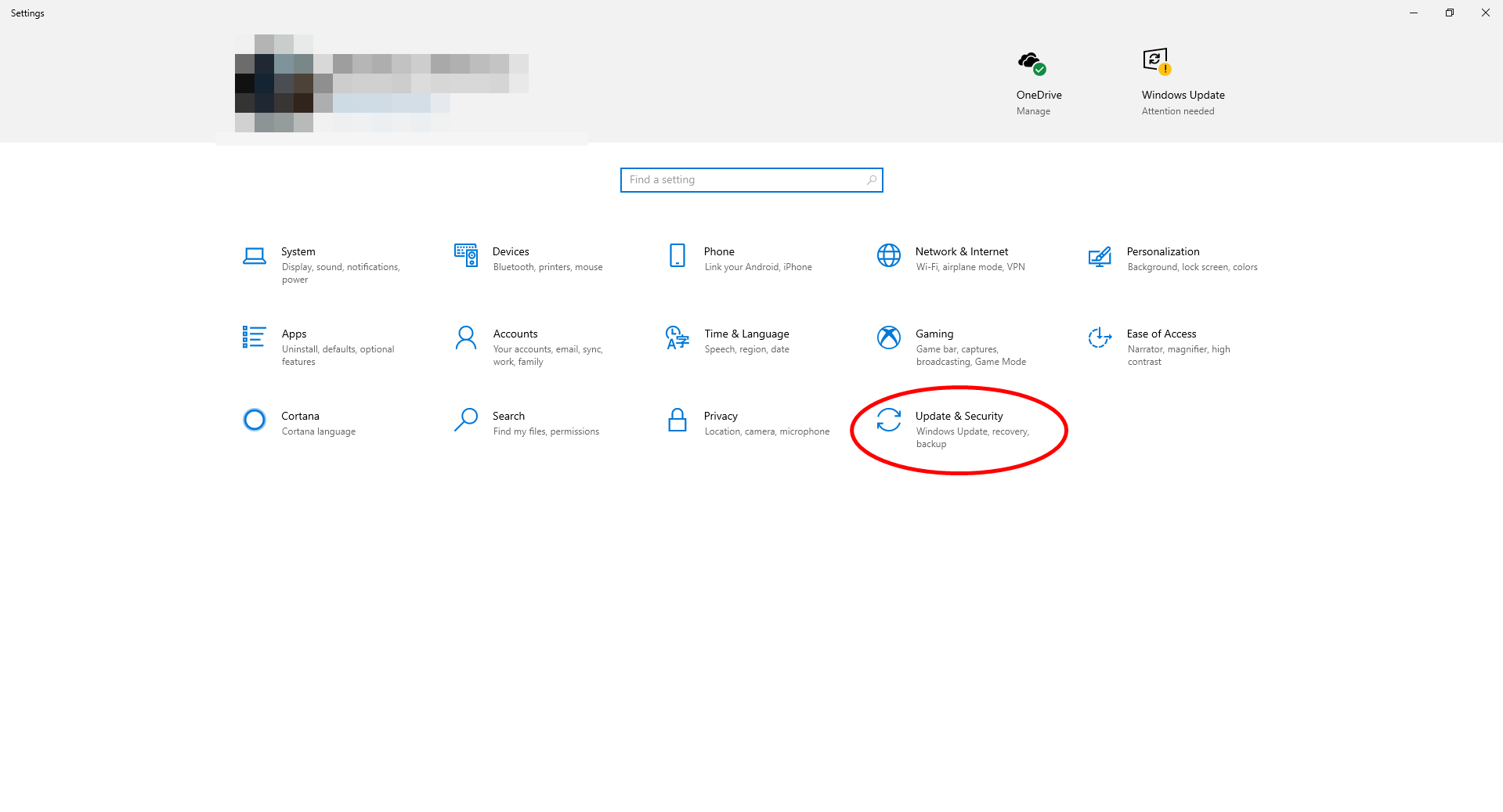
- Click on Windows Security from the left column.
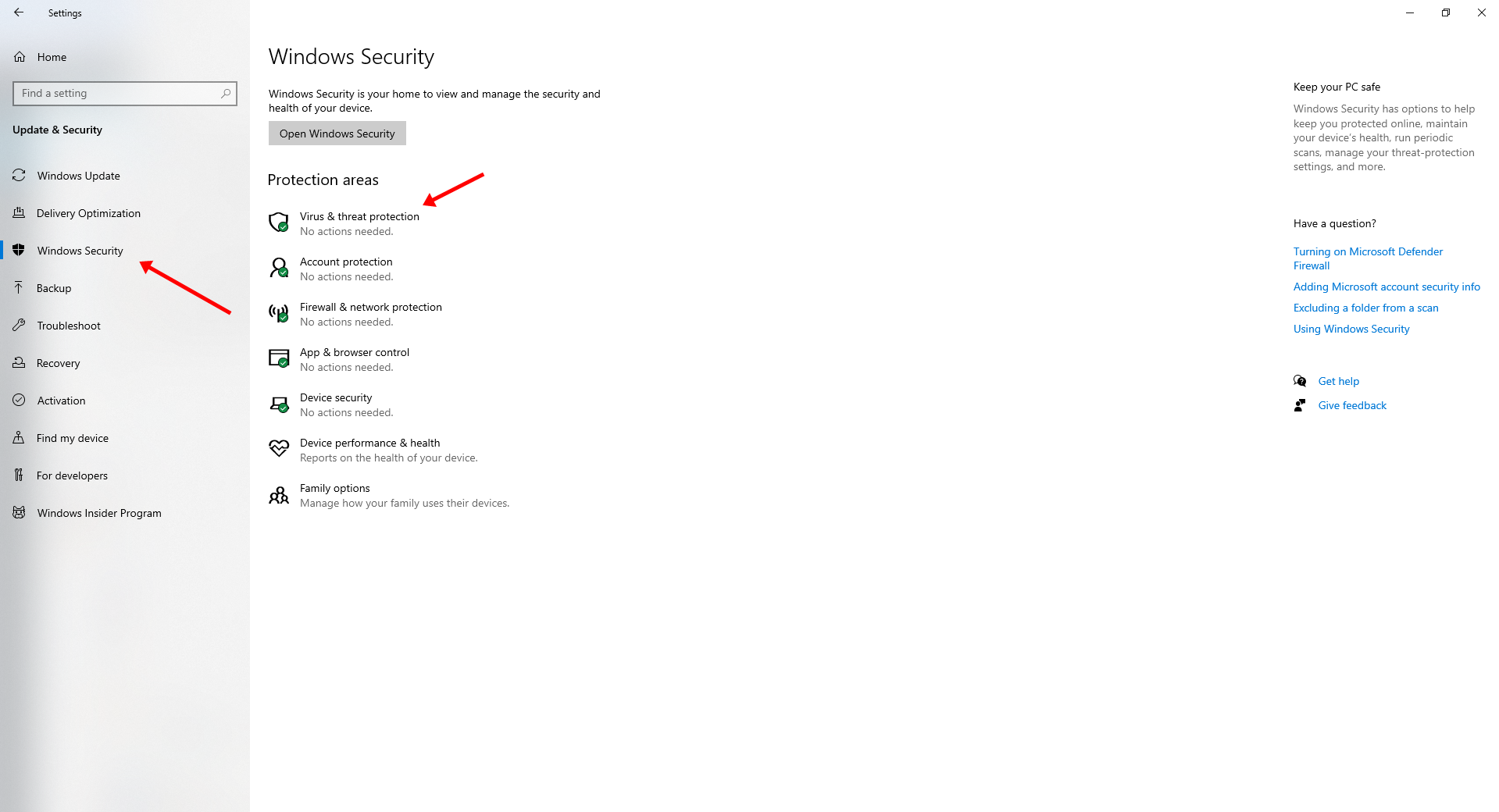
- Click on Virus & threat protection. A new window will appear.
- Click on Manage settings under the Virus & threat protection section.
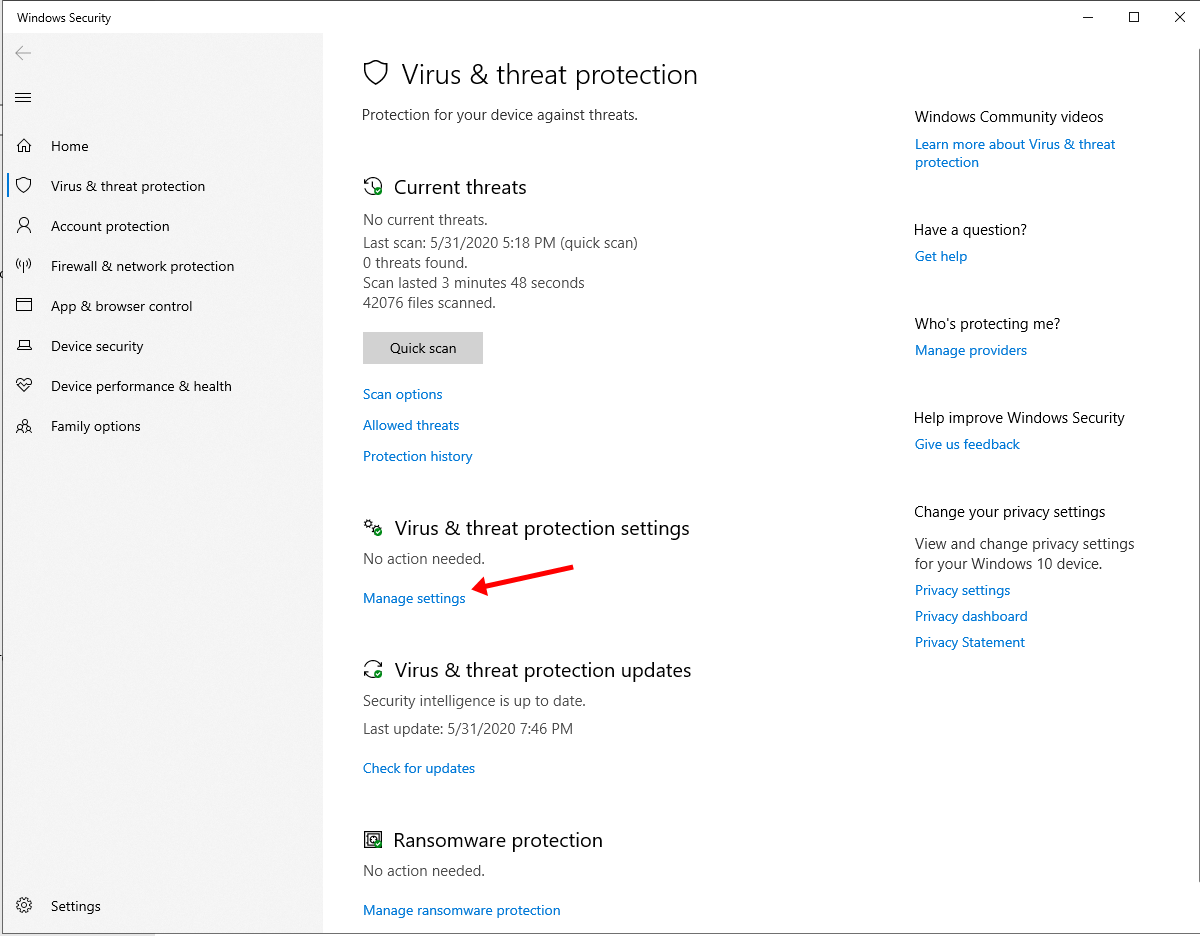
- Click on the Add or remove exclusions option under the Exclusions section.
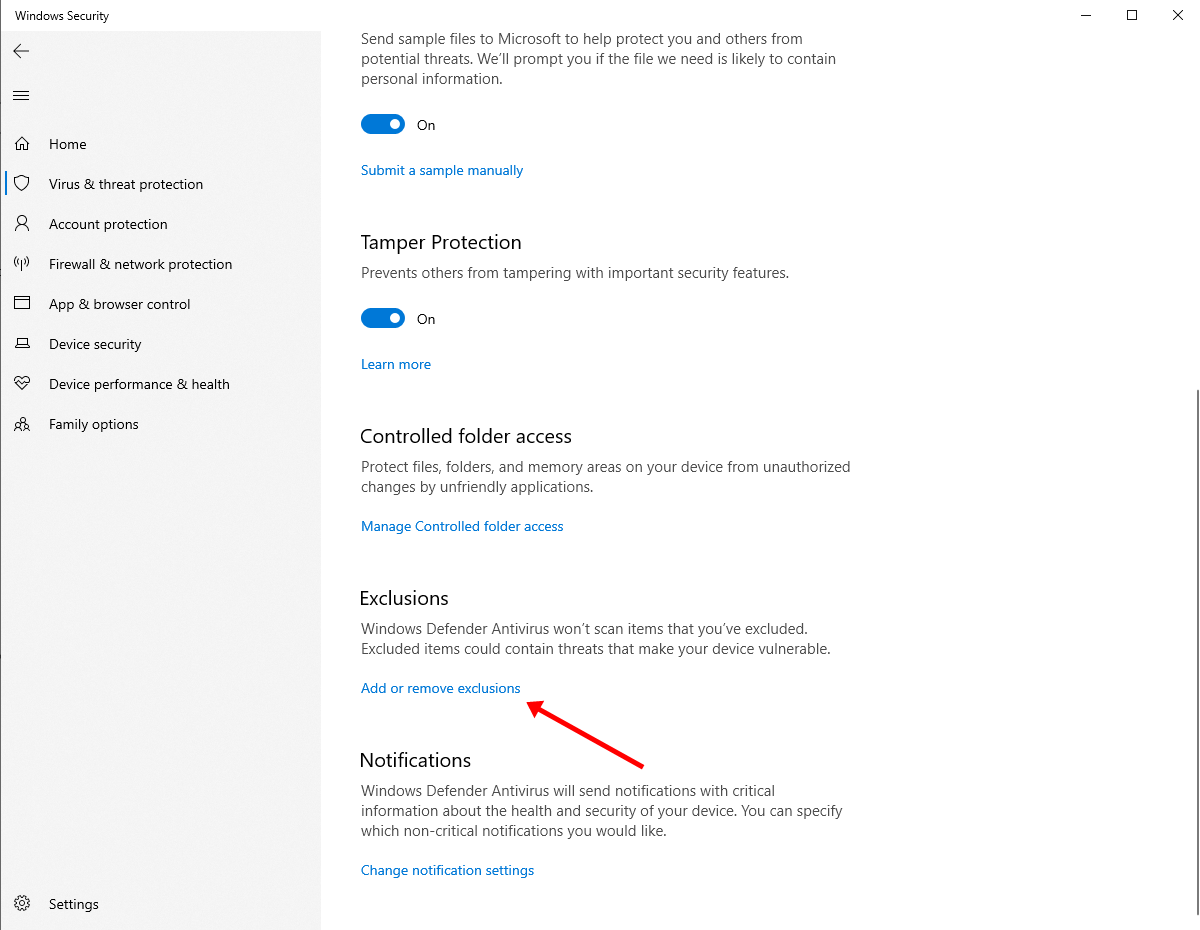
- Click on Add an exclusion > Process.
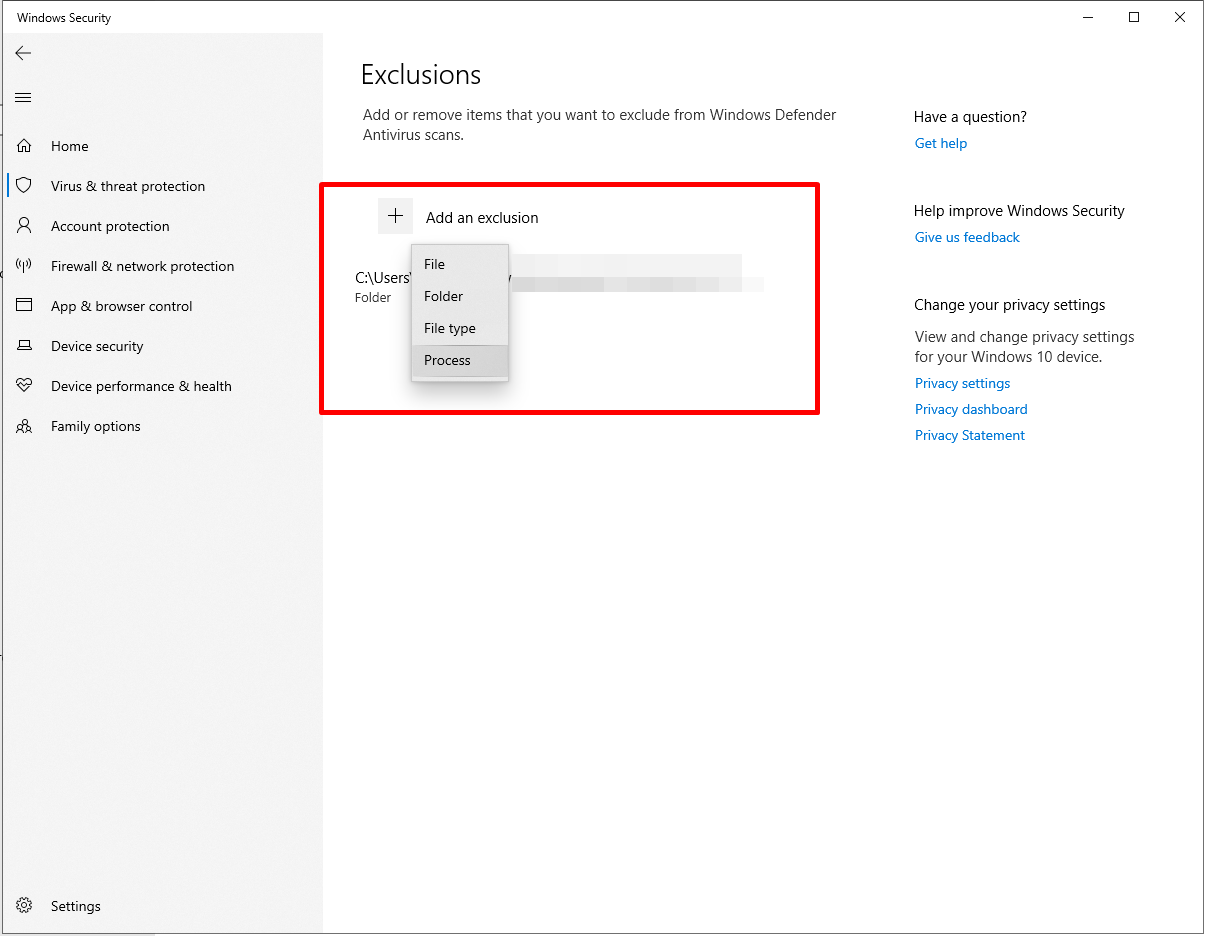
- Now, type MsMpEng.exe and click Add.
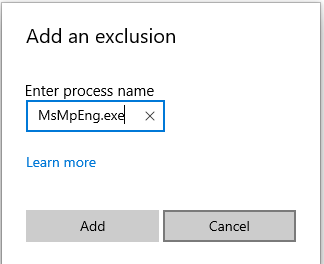
Adding MsMpEng.exe to the Windows Defender exclusion list reduces the CPU resources consumption. If this fix didn’t work for you then move on to the next one.
Fix 3: Disabling Windows Defender
If the aforementioned two fixes didn’t work for you and you are still facing the issue then you should try disabling Windows Defender, this will disable Windows Defender services throughout but the problem will be resolved. Here is how you can disable Windows Defender.
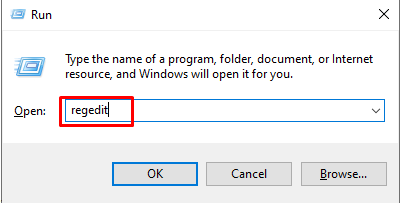
- Open the Run box by pressing Windows + R key at the same time.
- In the Run box, type regedit and hit Enter.
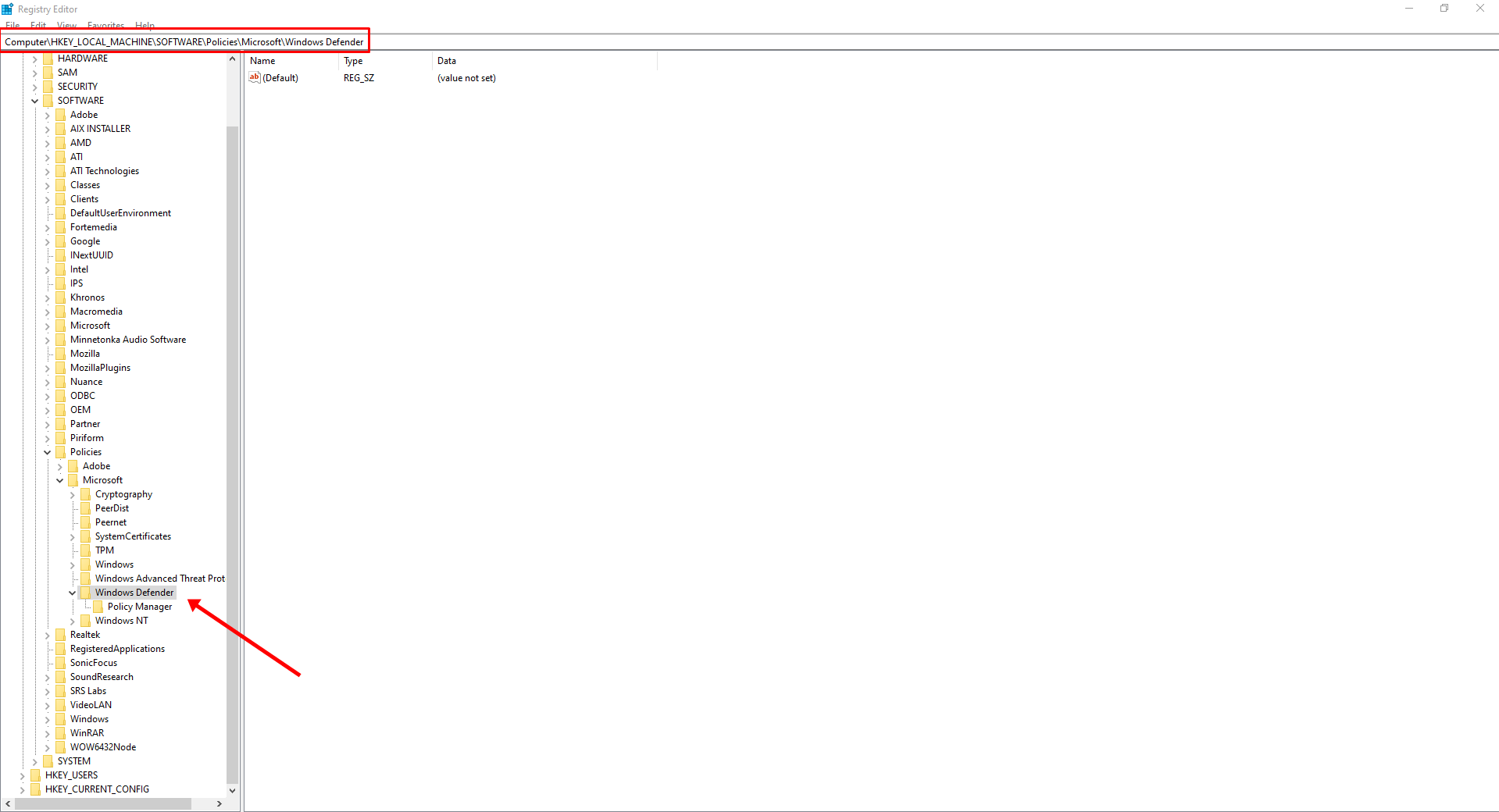
- From the left navigation column, go to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender.
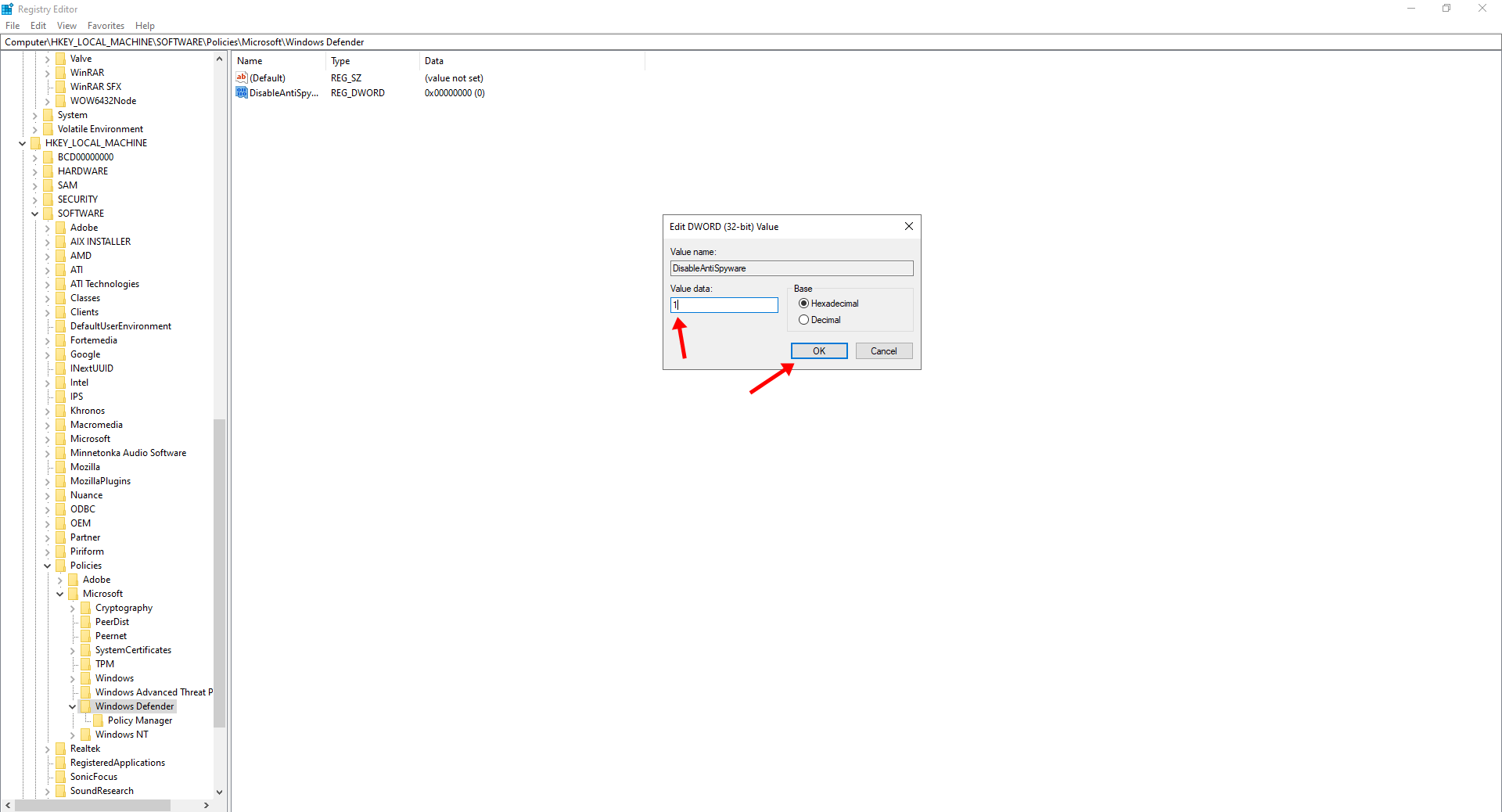
- Look for a registry entry named DisableAntiSpyware and double click on it.
- Set the value data for the DisableAntiSpyware registry to 1 and click on OK.
- If you don’t see a registry entry named DisableAntiSpyware then right-click in the main Registry Editor pane and select New > DWORD (32 bit) Value.
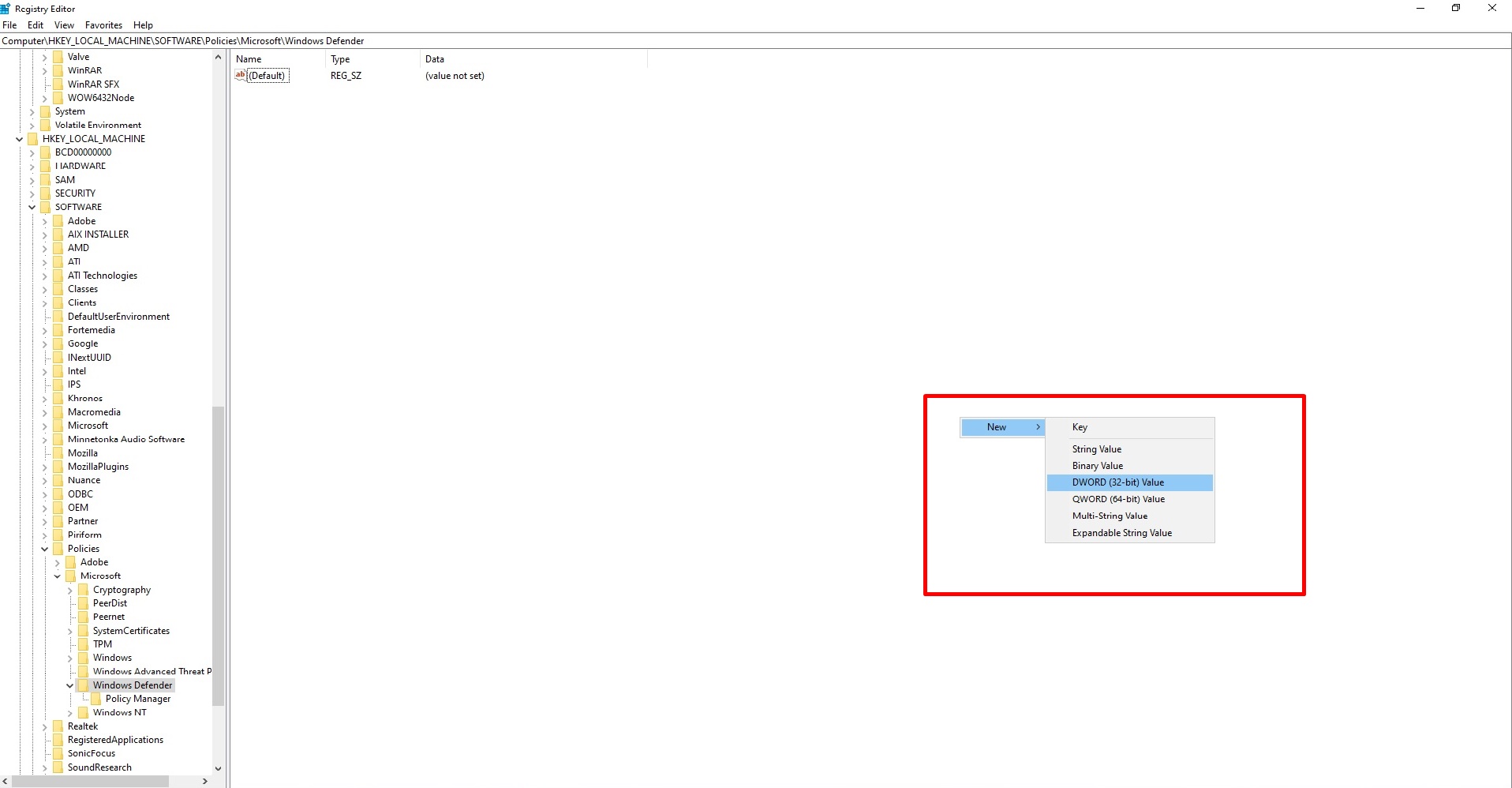
- Name this registry entry DisableAntiSpyware.
- Now, double click on the newly created registry entry and set its value data to 1 and click OK.

When you use this solution then it will completely disable Windows Defender and all the related processes and services including Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe. So, to keep your PC protected against viruses, you will have to install any other antivirus program which will consume fewer resources than Windows Defender.
